cloud bursting
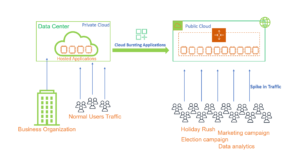
In real world environments sometimes, we come across scenarios where customers private cloud infrastructure running at in-house, or Colo datacentre environments is not able to efficiently manage the workloads with seasonal load spikes or varied demand patterns. This problem can be solved by using cloud bursting which dynamically uses hybrid cloud to scale up the infrastructure on demand.
What is cloud bursting
Cloud bursting is a technique which is used in hybrid cloud models to dynamically scale an application workload to public cloud (like AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure etc) when the existing private cloud resource utilization capacity reaches a certain threshold. In other words, if the private cloud infrastructure can process the demand, the workloads run exclusively on it but when additional compute power is needed, it bursts the extra workload to public cloud setups. This way, the primary deployment is managed by private cloud and public cloud resources are only used to accommodate demand spikes. Once the load reduces back to normal levels, compute capacity is scaled down by decommissioning public cloud.
Cloud Bursting Architecture –
The core foundation of cloud bursting architecture lies on automated scaling listener and resource replication mechanisms. It exhibits a form of flexible scaling methodology that supports scaling out on-premises IT resources into public cloud whenever there is a demand spike and on-premises resources breaches the pre-configured capacity thresholds. The public cloud resources become active only when there is high usage demand and are released once the traffic returns to normal. Request redirection to cloud is regulated by automated scaling listener and resource replication is used to attain resource state synchronisation between two environments.
Popular cloud bursting approaches are:
- Manual Bursting – As name suggests it enables the cloud administrators to manually provision and de-provision the cloud resources and services. The load-balancer determines when to notify the administrator based on configured capacity thresholds. It finds suitability with scenarios needing large scale temporary cloud deployments or when existing on-premises resources needs to be freed up for other business critical application. Once the demand returns to normal the public cloud deployment is destroyed to attain financial efficiency.
- Automated Bursting – In automated deployments the bursting process is managed by setting up automated policies which enables the application platform to take provisioning and de-provisioning decisions. IaC (Infrastructure as code) tools like terraform, configuration managements tools like ansible, puppet, chef, container orchestration tools like Kubernetes etc are utilised for triggering events and setting up and destroying public cloud environments with changing business demands.
- Distributed load balancing – Here the application is configured to operate between a public cloud and a data centre. Mostly stateful resources are kept in-house and shared between both public and private compute resources (else redundancy and synchronisation mechanisms are used to maintain application accuracy). The application is deployed both locally and in public cloud and load balancing operations are used to share traffic.
Advantages of Cloud Bursting –
1) Flexibility – It offers great flexibility to the business as it can quickly adapt to the changing business needs. Private cloud resources can be freed when needed and utilised for more critical in-house short-term operations.
2) Cost – It offers a business the advantage to keep its private cloud infrastructure in minimalistic state. For public cloud, the business pays only for the compute it utilises.
3) Business continuity – It helps to create a seamless experience for users as during high spikes in demand the traffic is bursts to public cloud without downgrading the application performance.
Cloud Bursting use cases –
- Festival sales or holiday rush for digital retail platforms or shopping websites
- New product launches over a wider geographical region
- Fundraising campaigns around election times
- End of business quarters or annual clearance sales
- Workloads involving big data analytics or machine learning modelling tasks
- Manage traffic on online gaming platforms
